Different Applications Vulnerabilities
HTTP File Server (HFS) 2.3
scanning
┌──(root㉿INE)-[~]
└─# nmap -sV -p 80 demo.ine.local
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-12-01 21:14 IST
Nmap scan report for demo.ine.local (10.5.16.210)
Host is up (0.0030s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 6.48 secondsLet us find the if we have an exploit
searchsploit hfs
Rejetto HTTP File Server (HFS) 2.3 is vulnerable to RCE. Exploiting the target server using the Metasploit framework

Manual Exploitation
Now that we have identified a vulnerable service running on the target system, we can search for publicly available exploit code that can be used to exploit Rejetto HFS 2.3 with Searchsploit.
This can be done by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, Searchsploit reveals quite a few exploits, one of which is a Metasploit module, however, in our case, we will be using the Python exploit.

Now that we have identified the exploit we would like to use, we can copy the exploit file to our current working directory with Searchsploit by running the following command:
This exploit, while functional, does not work out of the box and needs to be modified per the environment you are working in and the configuration of the target.
Now that we have copied the exploit to our current working directory, we can modify it with VIM by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, this exploit requires you to change the local IP and local port values.

You can obtain your local Kali IP address by running the following command:
As shown in the preceding screenshot, we have changed the local port to 1234, feel free to change this to any open port on your Kali system.
After making the changes to the exploit code, you can save it and exit out of VIM.
After modifying the exploit code, we can run it with Python to ensure that it works correctly.
For this exploit to work, you will need to host the nc.exe on a web server as the exploit will download it to the target system.
Kali Linux comes pre-packaged with various Windows binaries, one of which is the nc.exe executable found under /usr/share/windows-resources/binaries/nc.exe.
We can copy the nc.exe executable to our Desktop by running the following command:
After copying the nc.exe executable to the Desktop, we can host it by setting up an HTTP server on port 80 with Python. This can be done by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, this will host the nc.exe executable.

Next, we will need to open a new terminal window where we will set up the Netcat listener to receive the connection from the target once the exploit script is executed.
We can set up the Netcat listener by running the following command:
Note: Ensure you change the Netcat port to listen if you specified a different port when modifying the exploit.
After setting up the web server and the Netcat listener, you will need to open another terminal window to run the exploit script.
Navigate to the directory you copied the exploit to with Searchsploit and run the following command:
Note: You may need to run the exploit multiple times for success!
As shown in the following screenshot, if the exploit script runs successfully, you should receive a reverse shell on your Netcat listener.

Badblue
Scanning
BadBlue 2.7 is available.
We will search the exploit module for badblue 2.7 using searchsploit.

There is a metasploit module for badblue server. We will use PassThru remote buffer overflow metasploit module to exploit the target.

Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat is a Java web server that primarily serves as a servlet container, which means it provides an environment for running Java-based web applications.
Target is running a Tomcat Server 8.5.19. Search “apache tomcat 8.5.19 exploit”

Target is running a Tomcat Server 8.5.19. Search “apache tomcat 8.5.19 exploit” on google to find the vulnerability.

Open exploit-db.com link: [https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/42966]

The target might be vulnerable to “JSP Upload Bypass RCE”.
Exploiting the target server using metasploit tomcat_jsp_upload_bypass module.
Commands:

We have successfully exploited the target Tomcat server and received a shell.
Roxy-WI
As we can see in the Nmap result under the HTTP title, Roxy-WI is running on the web server. Let's check if there is an exploit available for it in Metasploit. We can search for it using the following command:

Here, we have found an exploit. Let’s select this module by typing use 0, and then type options to see the required parameters we need to exploit this.
We only need to set LHOST and RHOSTS.
LHOSTis your local IP, which you can obtain by runningifconfig.RHOSTSis our target system.
After setting these, type exploit to run the exploit.

Xdebug Extension
Step 1: We will scan the target using dirb tool.

Step 2: We will access phpinfo.php file using curl to find more information about the web server.

Step 3: The xdebug extension is enabled on target server. We can exploit it using exploit/unix/http/xdebug_unauth_exec metasploit module.

Process Maker
Now that we have been able to identify what web application is running on the web server and the respective version of the web app, we can utilize a tool like Searchsploit to identify whether this specific version of ProcessMaker is vulnerable to any exploits.
This can be done by running the following command:

As shown in the preceding screenshot, a Metasploit Framework exploit module exists for the ProcessMaker web app, however, it does not specify what version it can be used to exploit. As a result, we will need to fire up the Metasploit Framework console and test the exploit.
We can access the Metasploit Framework via the infamous Metasploit Console (msfconsole).
This can be done by running the following command:

Once msfconsole has started, we can search for the ProcessMaker exploit module by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, the search reveals two exploit modules, in this case, we will be using the first exploit listed.

We can use this module by running the following command:
After loading the module, we will need to configure the module options following the target system we are exploiting. You can display the options pertinent to a module by running the following command:

Firstly, we will need to set the target address, this can be done by running the following command:
Command:
Upon closer inspection of the module options, we can identify that this module requires legitimate credentials to work correctly. Fortunately, we were able to identify the default credentials for the admin user. In this case, the module already has the USERNAME and PASSWORD options set to admin.
After configuring the RHOSTS option, we can execute the module by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, if the exploit runs successfully, we should receive a meterpreter session providing us with remote access to the target system.

Exploiting flatcore
Since the website is running on Flatcore, we should check if there are any known exploits available for this CMS. We can do this using the following command:
This command searches the Exploit-DB database for publicly available exploits related to Flatcore. If an exploit is found, we can analyze its details and attempt to use it for further exploitation.

As you can see, there are two available exploits, but neither is present in Metasploit. This means we need to execute the exploit manually on our system. Since our goal is to gain access to the root system, we will use the first exploit, which is Remote Code Execution (Authenticated).
To copy the exploit’s Python code into our current working directory, we can use the following command:
Before executing the exploit, we should first read and analyze the code to understand how it works.

After reviewing the code, we can determine how to execute the exploit. To run the Python script and attempt exploitation, we use the following command:

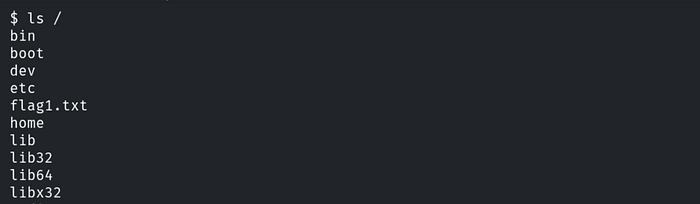
We have successfully logged in using the exploit. Now, to retrieve our first flag, we need to access the root directory. First, we list the directory contents using the following command: ls /
PHP Exploitation
We can identify the version of PHP running on the web server by accessing the phpinfo.php file in a browser as shown in the following screenshot.

The phpinfo.php file reveals that PHP 5.2.4 is running on the web server.
Now that we have identified the exact version of PHP running on the web server, we can utilize a tool like Searchsploit to find exploits affecting this version of PHP.
This can be done by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, the Searchsploit search reveals quite a few exploits, however, one stands out as a potentially useful exploit.

This exploit is available as a Metasploit framework exploit module.
We will need to start the Metasploit Framework console (msfconsole) in order to use this exploit, this can be done by running the following command:
We can now load the module by running the following command:
After loading the module, we will need to configure the module options, more specifically, we will need to set the target.
We can now execute the exploit module by running the following command:
As shown in the following screenshot, the exploit runs successfully and provides us with a meterpreter session on the target system.

Last updated